What is Trochanteric Bursitis?
Trochanteric bursitis is the most common bursitis of the hip. Trochanteric bursitis is inflammation of the bursa (a small, cushioning sac located where tendons pass over areas of bone around the joints), which lies over the prominent bone on the side of your hip (femur).
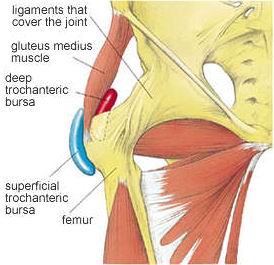
The superficial trochanteric bursa is located over the greater trochanter. This is the most commonly inflamed bursa. A deep trochanteric bursa lies deeper and can become inflamed in more severe cases.
What are Trochanteric Bursitis Symptoms?
One or more of the following symptoms may be experienced:
- Pain and swelling occurring over the side of the hip
- Referred pain that travels down the outside thigh and may continue down to the knee
- Pain when sleeping on your side; especially the affected hip
- Pain upon getting up from a deep chair or after prolonged sitting (eg. in a car)
- Pain when climbing stairs
- Pain in sitting with the legs crossed
- Increased pain when walking, cycling or standing for long periods of time
What Causes Trochanteric Bursitis?
The trochanteric bursa may be inflamed by a group of muscles or tendons rubbing over the bursa and causing friction against the thigh bone. This injury can occur traumatically from a fall or a sport-related impact contusion.
It can also be a case of gradual onset via a repetitive trauma to the bursa from such activities as running (with poor muscles control or technique), walking into fatigue, or cycling, especially when the bicycle seat is too high.
It is also a secondary injury associated with chronic conditions such as:
- Scoliosis – curvature of the spine
- Unequal leg length
- Weak hip muscles
- Osteoarthritis (degenerative joint disease) of the hips or lower back
- Calcium deposition in the gluteal tendons that run over the bursa
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
How is Trochanteric Bursitis Diagnosed?
Your Podiatrist will provide you with an assessment of your medical history and a physical examination of your hip, pelvis and back. A hallmark sign is if you feel tenderness over the bursa or greater trochanter (hip bone) when pressure is applied.
What is Trochanteric Bursitis Treatment?
Ice
Bursitis is an inflammed bursa. Daily application of ice packs is highly recommended to reduce your pain and swelling.
Medications
NSAIDs or anti-inflammatory drugs (i.e. ibuprofen). Use of these medications should be discussed with your doctor.
Corticosteroid Injections
Single injection of a corticosteroid with a local anaesthetic into the bursa may be required to stimulate your healing response. It is preferable to have this injection using ultrasound guidance.
EWST Shockwave therapy
Shockwave therapy delivers acoustic soundwaves to the affected area causing the body to regenerate the damaged collagen, dramatically speeding recovery from Hip bursitis.
Trochanteric Bursitis Treatment
PHASE I – Pain Relief & Protection
Managing your pain. Pain is the main reason that you seek treatment for trochanteric bursitis.
Your Podiatrist will use an array of treatment tools to reduce your pain and inflammation. These include: ice, EWST Shockwave therapy, de-loading taping techniques, and in severe cases temporary use of a mobility aid (eg cane or crutch) to off-load the affected side.
PHASE II – Restoring Normal ROM, Strength
As your pain and inflammation settles, your podiatrist will turn their attention to restoring your normal hip joint range of motion, muscle length and resting tension, muscle strength and endurance, proprioception, balance and gait (walking pattern.
Hip researchers have discovered the importance of your hip muscle muscle strengthening and retraining of the muscles which stabilise the hip structure. Your Podiatrist will assess your muscle strength and stability and prescribe the best exercises for you specific to your needs.
PHASE III – Restoring Full Function
The final stage of your rehabilitation is aimed at returning you to your desired activities. Everyone has different demands for their hips that will determine what specific treatment goals you need to achieve. For some people, it simply be to walk around the block. Others may wish to run a marathon.
Your Podiatrist will tailor your hip rehabilitation to help you achieve your own functional goals.
PHASE IV – Preventing a Recurrence
Trochanteric bursitis does have a tendency to return. The main reason it is thought to recur is due to insufficient rehabilitation.
In addition to your muscle control, your Podiatrist will assess your hip biomechanics and start correcting any defects. It may be as simple as providing your will core abdominal exercises or some foot orthotics to address any biomechanical faults in the legs or feet.
Fine tuning your hip stability and function by addressing any deficits in core strength and balance, learning self-management techniques and achieving the ultimate goal of safely returning to your previous sporting or leisure activities!
Trochanteric Bursitis Surgery
Surgery is not a common path. However, in persistent cases, arthroscopic removal of the bursa; a bursectomy, can be performed.
What Results Can You Expect for Trochanteric Bursitis?
While some people can respond quickly to physiotherapy treatment within a few weeks, more chronic cases where a tendinopathy exists in the gluteal muscle group under the bursa can require a few months to achieve recovery.
Trochanteric bursitis is successfully managed in the vast majority over a period of approximately six-weeks. It is important to not stop your rehabilitation exercises as soon as you pain abates.
Excellent hip muscle control and normal foot, and leg posture is your best rehabilitation and prevention strategy



